BRENTWOOD, Tenn. (BP) — Visiting a friend outside his hometown of Gloucester, England, in the late 1700s, Robert Raikes encountered children cursing, gambling and fighting in the streets. He was horrified, but a local woman told him it was even worse on Sundays, the children’s one day off each week from the factory. Determined to help children in that situation learn to read and learn about the God who loved them, Raikes founded the first Sunday school in 1780.
While much has changed in the past 250 years, churches are still using some form of small-group discipleship to help children and adults grow in their faith. And most churches still use the term Sunday school to describe at least part of their ministry.
According to a Lifeway Research study of U.S. Protestant churches with ongoing adult Bible study groups, 56% say the label “Sunday school” describes at least part of their groups ministry. Almost 3 in 4 (72%) say they are comfortable with others referring to their groups as adult Bible studies. Around 2 in 5 (39%) say small groups. Fewer say the terms adult Bible fellowships (13%), life groups (13%) or connect groups (10%) fit their ministry.
“When it comes to Bible study groups, it’s less about the name we give the ministry and more about what the groups actually do,” said Ken Braddy, director of Sunday school and network partnerships at Lifeway. “If a group learns and obeys God’s Word, invites others to follow Jesus, forms deeper relationships and engages in acts of service inside the church and out in the community, you can call a group ministry whatever you like.”

Group makeup
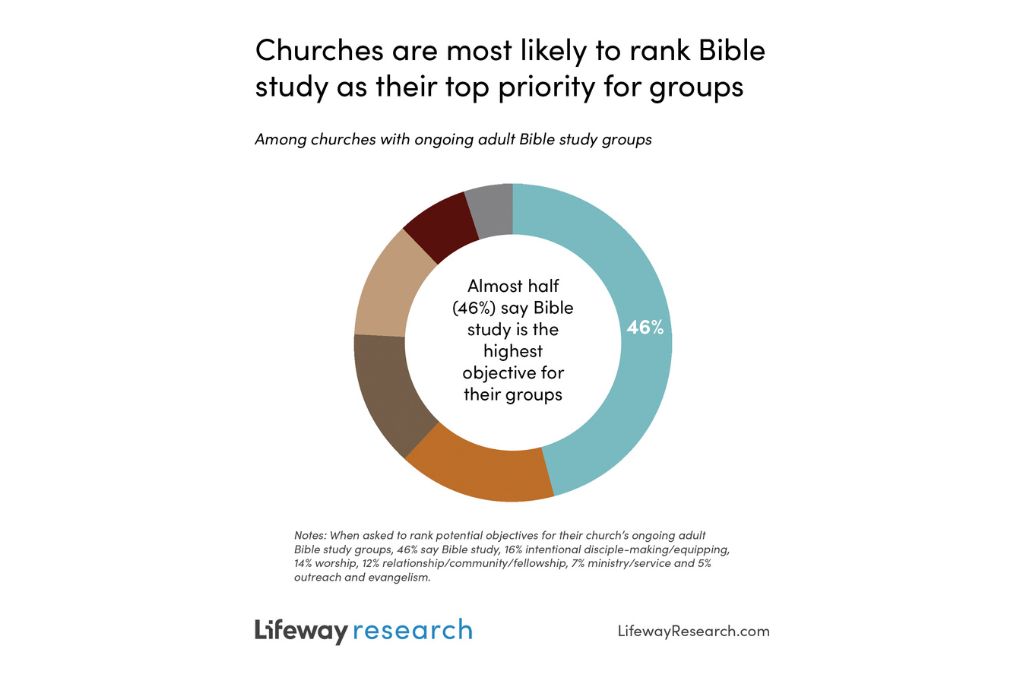
When these groups gather, leaders are most likely to say they want the primary focus to be on studying Scripture. Almost half (46%) of adult Bible study group ministry leaders say Bible study is the highest objective for their groups. Fewer say the primary purpose is intentional disciple-making or equipping (16%), worship (14%), relationships/community/fellowship (12%), ministry/service (7%) or outreach and evangelism (5%).
On average, churches have seven ongoing Bible study groups for adults with an average of 69 weekly participants. In a three-month period, the average church sees 91 individuals connect with a small group Bible study at least once.
Around 2 in 5 worship attendees at the average church (44%) also typically participate in small groups. A third of churches (33%) say at most a quarter of their worship service attendance is involved in an ongoing adult Bible study. Another third (34%) say they have more than a quarter but no more than half. The final third (33%) have at least half of their worship attendees involved in their small group ministry, including 14% who say more than 3 in 4 attend both the worship service and a small group.
“Involvement in worship and small groups are not in competition. Studies have shown participation in ongoing Bible studies bolsters worship attendance,” said Scott McConnell, executive director of Lifeway Research. “The higher a church’s percentage of weekend worship attendees involved in a small group, Sunday school class or similar group, the more likely worship attendance growth is over a 5-year period.”
Time and place
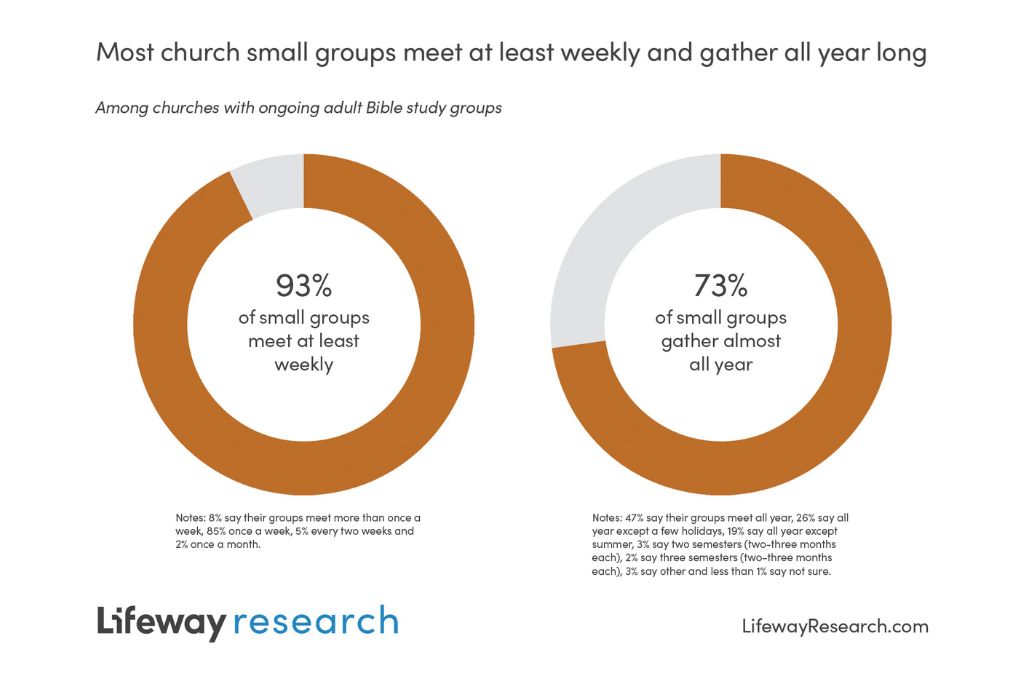
Almost every church leader (93%) says their ongoing groups are meeting at least weekly, including 85% who say once a week and 8% more than once a week. Fewer say they gather every two weeks (5%) or once a month (2%).
For around three-quarters (73%), those gatherings are happening basically all year long. Almost half (47%) say they meet all year, while another 26% say they meet all year except a few holidays. Around 1 in 5 (19%) take the summers off but otherwise meet the rest of the year. Fewer group ministry leaders say they meet for two semesters of two to three months (3%) or three similar length semesters (2%). Only 3% say their church has some other type of meeting schedule.
More than 9 in 10 leaders (92%) have groups gathering at the church building or whatever location the congregation meets in for worship. Fewer than 1 in 3 (31%) say at least some groups meet in homes, while 13% use various off-campus locations. On average, churches say 4 in 5 groups (79%) meet at the church.
Three in 10 say their groups exclusively meet before or after their weekly worship service. Another 35% of churches meet any day or night of the week other than when they regularly gather for worship. A similar percentage (36%) say they have groups gathering both before or after services and other times during the week.
“The way churches choose to operate their adult ongoing groups fits their focus,” McConnell said. “Leaders of adult groups ministries prioritize Bible study, relationships and intentional disciple-making as objectives of ongoing groups. It is not surprising that these groups meet frequently, break infrequently and stay together, reinforcing their goals of living in disciple-making relationships.”
Organization
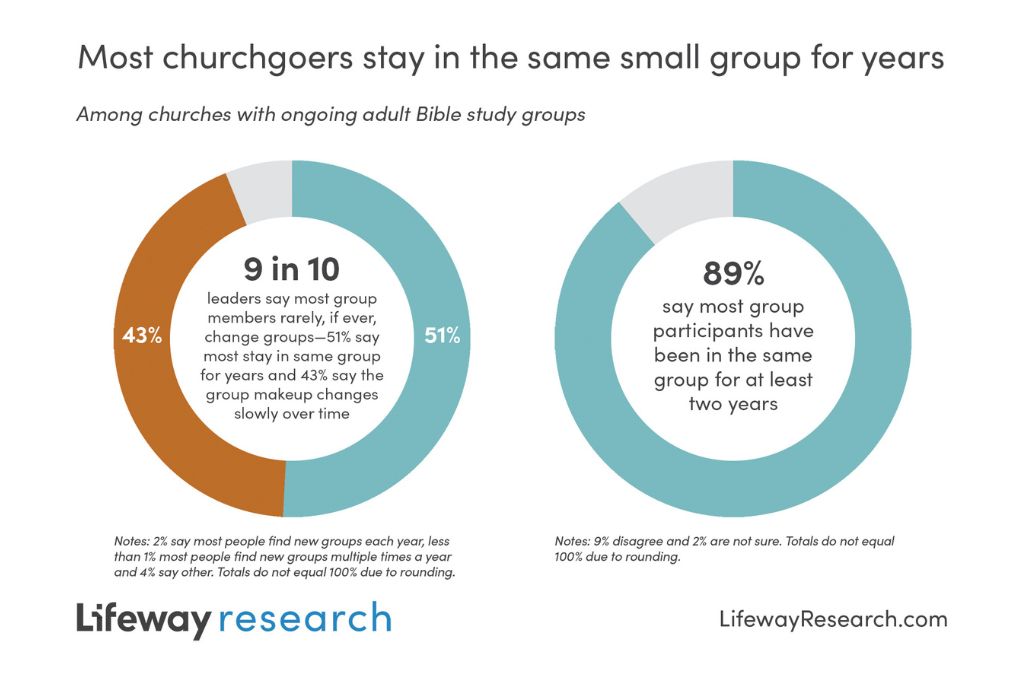
Most churchgoers find a group and stick with it. Half of the group ministry leaders (5 %) say most of the people at their church stay in the same group for years, while 43% say the makeup of the group changes slowly over time. Few say most people find a new group each year (2%) or multiple times a year (<1%). Almost 9 in 10 leaders (89%) say most group participants have been in the same group for at least two years.
The lack of change may be due to the lack of new options. Around a third (34%) of leaders say they’ve started new ongoing adult Bible study groups in 2024. Two-thirds (66%) have not.
Group participants may also remain in the same groups because they’ve found other churchgoers with whom they share similarities. Almost half of leaders (45%) say their groups are organized by an interest in the topic being studied. Around 3 in 10 organize around age (31%), life stage (29%) and gender (28%). Another 22% have an affinity or shared interest, while 10% meet together because of their geographic location. Just 1 in 10 (10%) are organized based on an assignment by the pastor or elders. For some (11%), their church only has one class. Around 1 in 6 (17%) have some other organization method.
Size
If a group starts to grow, most leaders aren’t going to intervene. Nine in 10 say they do not limit the size of ongoing adult Bible study groups. Experts, however, suggest groups that grow too large should be split to form new groups for several reasons.
“Churches would be wise to strongly encourage groups to remain small to medium-sized,” said Braddy. “It’s easier to recruit new group leaders because larger groups are intimidating to lead. Discipleship happens best within a smaller group of people. Jesus had a group of 12 and an inner group of three. And group members often have deeper relationships in smaller groups because they are known. It’s hard to hide in plain sight, but people can disappear in larger groups.”
Some leaders may not be looking to split up larger groups because they aren’t sure exactly who is in their church’s groups. Around half (53%) say they track attendance in their adult Bible study groups. Only slightly more (56%) say they maintain a roster of who is in each group.
For those that do have a roster or take attendance, most are doing so using the most traditional means. Around 2 in 3 (64%) say their record keeping involves paper, including 37% who say it is all on paper and 28% who say they use paper and spreadsheets. Three in 10 (30%) say they use some type of group management software, including 20% that have a phone app.
“Caring requires intentionality,” said McConnell. “Tracking adult small group attendance provides an easy prompt to a group that when someone has missed multiple meetings, they should be told they were missed. This data also provides groups ministry leaders a view of how engaged people are in their groups.”
For more information, view the complete report and visit LifewayResearch.com.
Methodology
The online survey of 1,021 adult Bible study group ministry leaders was conducted May 27 – June 27, 2024. Contact lists of adult Bible study group ministry leaders and pastors were developed from both Lifeway’s lists and outside lists. Each interview was conducted with the person most responsible for Bible study groups for adults at the church. Each respondent was screened to ensure they were able to describe their church’s Bible study groups for adults and that their church is Protestant or non-denominational Christian in the U.S.
Southern Baptist churches were oversampled. The 639 SBC responses were weighted down to reflect their correct proportion of Protestant churches. Responses were weighted by region, church size and denominational category to more accurately reflect the population. The completed sample is 1,021 surveys. The sample provides 95% confidence that the sampling error does not exceed plus or minus 4.6%. This margin of error accounts for the effect of weighting. Margins of error are higher in sub-groups.
Limitations: Probability samples for Protestant adult Bible study group ministry leaders do not exist. When representative sampling is not possible, it is important to obtain as wide a variety of respondents as possible. Three broad sources were used:
- Protestant pastors who have opted in for future research on previous probability surveys
- Southern Baptist ministers of education, Sunday school directors and discipleship directors shared by congregations as part of the Annual Church Profile census
- Adult Bible study group ministry leaders who have interacted with Lifeway’s research, events or communications
Note that some groups are less represented because the scope of this study does not include churches that do not have adult Bible study group ministry activities. Groups that interact with Lifeway less will be underrepresented in this study. Indications of the breadth of the sample prior to weighting include:
- Sizes of churches participating (21% <50, 25% 50-99, 25% 100-249, 29% 250+)
- Ages of respondents (33% 18-49, 37% 50-64, 30% 65+)
- Region of churches participating (5% Northeast, 23% Midwest, 64% South, 9% West)
(EDITOR’S NOTE — Aaron Earls is a writer for LifeWay Christian Resources.)


